- No products in the cart.
In the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries, maintaining stringent quality standards is paramount to ensuring the safety and efficacy of products. Cleanroom facilities, governed by current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP), play a crucial role in achieving these standards. In this blog post, we'll delve into the key cGMP requirements set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for cleanroom facilities and equipment, highlighting the measures industries must adhere to in order to ensure quality and compliance.
Understanding cGMP
Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) are regulations enforced by the FDA to guarantee the quality, safety, and effectiveness of pharmaceutical and medical device products. Adherence to cGMP is essential for manufacturers to obtain and maintain FDA approval.
Cleanroom Facilities and cGMP
Cleanrooms are controlled environments designed to minimize the risk of contamination during the manufacturing process. The FDA mandates that cleanroom facilities comply with cGMP requirements to ensure the production of high-quality, uncontaminated products. These requirements encompass various aspects, including:
Cleanrooms are classified according to the maximum allowable concentration of airborne particles. The most stringent classification, ISO 5, is reserved for areas where highly sensitive products are handled.
2. Facility Design and Construction:
Cleanroom facilities must be designed to minimize contamination risks. This includes considerations such as:
- Smooth, non-porous surfaces
- Proper air filtration systems
- Controlled access points
- Separate airlocks and gowning areas
- Adequate lighting and ventilation
- Clearly defined work zones
3. Equipment Design and Maintenance:
Cleanroom equipment must be:
- Made of materials compatible with cleaning and disinfecting procedures
- Designed to minimize particle generation and contamination
- Regularly cleaned, calibrated, and maintained
- Documented procedures for cleaning and maintenance
4. Environmental Monitoring and Control:
Maintaining a controlled environment is crucial for cleanroom effectiveness. This involves monitoring and controlling factors such as:
- Airborne particle concentration
- Temperature and humidity
- Air pressure differentials
- Microbial contamination levels
5. Personnel Training and Gowning:
Personnel working in cleanrooms must be trained in proper procedures to minimize contamination risks. This includes training on:
- Gowning techniques
- Aseptic handling of materials
- Cleaning and disinfection procedures
- Emergency response procedures
Cleanroom PPE and Supplies Needed for Compliance
In addition to the cleanroom facility and equipment discussed earlier, ensuring cGMP compliance also requires the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and supplies. This crucial element helps to minimize contamination risks and protect personnel working in the cleanroom.
Essential Cleanroom PPE:
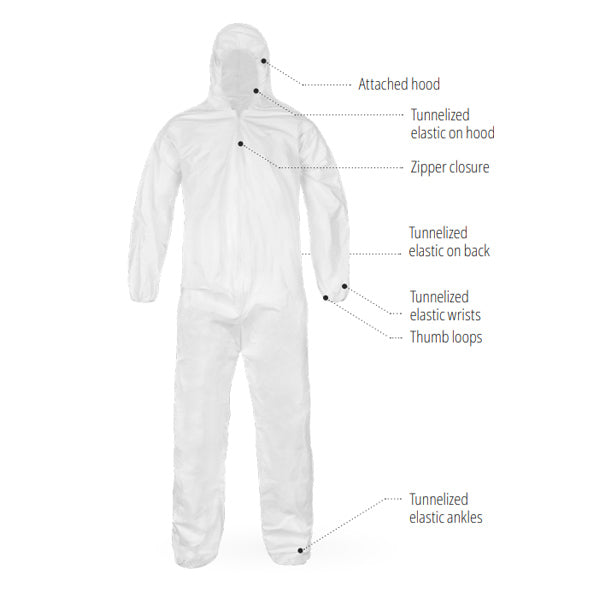
- Gowns: These disposable garments cover the entire body, preventing skin and clothing particles from contaminating the cleanroom environment. Different types of gowns are available depending on the required level of protection.
- Gloves: Cleanroom gloves protect both the wearer's hands from hazardous materials and the product from contamination. They are designed to be sterile and have excellent dexterity and tactile sensitivity.
- Shoe covers: These disposable coverings prevent contamination from shoes entering the cleanroom.
- Headwear: Hoods or bouffant caps are worn to cover the head and hair, minimizing the risk of particle shedding.
- Face masks or respirators: These provide protection against airborne contaminants and are especially important when handling hazardous materials.
- Eye protection: Safety glasses or goggles protect the wearer's eyes from splashes, dust, and other hazards.
Essential Cleanroom Supplies:
- Cleaning and disinfecting wipes: These pre-saturated wipes are used to clean surfaces and equipment within the cleanroom.
- Isopropanol alcohol: Used for disinfection and surface cleaning.
- Sticky mats: Placed at entrances and exits of the cleanroom to trap dirt and debris from shoes.
- Waste disposal containers: These specially designed containers are used to safely dispose of contaminated materials within the cleanroom.
Benefits of cGMP Compliance
Ensuring compliance with cGMP regulations offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced product quality and safety
- Reduced risk of product recalls and adverse events
- Increased patient trust and confidence
- Improved process efficiency and cost-effectiveness
- Improved compliance with regulatory requirements
Challenges and Solutions
Maintaining cGMP-compliant cleanrooms can present several challenges, including:
- High initial investment costs
- Ongoing operational and maintenance costs
- Stringent regulatory requirements
- Need for qualified personnel
- Risk of contamination due to human error or equipment malfunction
However, these challenges can be overcome through:
- Careful planning and design
- Investing in high-quality equipment and materials
- Implementing robust cleaning and disinfection procedures
- Providing comprehensive training for personnel
- Regularly monitoring and auditing cleanroom operations